.Explanation
We are given the function R(x)
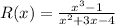
So, to get the vertical, horizontal, and oblique asymptote
Let us begin with the vertical assymptote
![\begin{gathered} For\:rational\:functions,\:the\:vertical\:asymptotes\:are\:the\:undefined\:points,\: \\ also\:known\:as\:the\:zeros\:of\:the\:denominator,\:of\:the\:simplified\:function. \end{gathered}]()
Thus
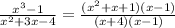
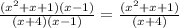
So, if we go by the definiation, the resulting function will be undefined when
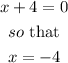
Therefore, the vertical asymptote is x = -4
For the horzontal asymptote
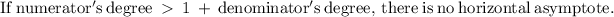
In our case,
The degree of the numerator is greater than the denominator, therefore, There are no horizontal asymptotes
For the oblique asymptote.
Oblique asymptote is also known as the slant asymptote
To get the oblique asymptote, we will have to simplify the expression as
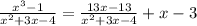
The rational term approaches 0 as the variable approaches infinity
Thus, the oblique asymptote is y =x−3