Solution:
Given:
Let the length of the shorter leg be represented by x.
Hence, using Pythagoras theorem,
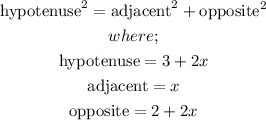
Hence,
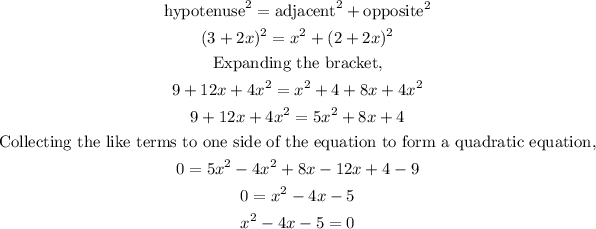
Factorizing the quadratic equation,
![\begin{gathered} x^2-4x-5=0 \\ x(x-5)+1(x-5)=0 \\ (x+1)(x-5)=0 \\ x+1=0\text{ OR x - 5 = 0} \\ x=0-1\text{ OR x = 0+5} \\ x=-1\text{ OR x = 5} \\ \\ Si\text{ nce the length of the side of a triangle can not be negative, then we ignore the negative value of x. Thus,} \\ x=5 \end{gathered}]()
Hence, the length of the three sides are;
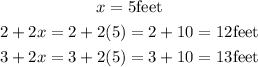
Therefore, the length of each of the three sides of the right triangle are;
5feet, 12 feet, and 13 feet.