1) List the known and unknown quantities.
Sample: carbon dioxide (CO2).
Volume: 250 mL.
Pressure: 1.0 atm.
Temperature: 22 ºC.
Ideal gas constant:
2) Set the equation
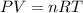
3) Converting units.
3.1-Convert ºC to K.
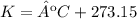
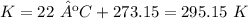
3.2-Convert mL to L
1000 mL = 1 L
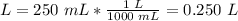
4) Plug in the known quantities