When two resistors are connected in series, their action is equivalent to a single resistor with an equivalent resistance which is the sum of the individual resistances:
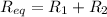
This means that the equivalent resistance must always be greater than any of the resistances that the series association is made of.
Since the current I, the resistance R and the voltage V are related through the following equation:
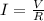
If we increase the value of R, then the value of I will decrease.
Therefore, adding another resistor in series will decrease the current through the circuit.