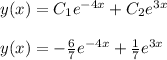Answer:
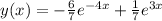 (See attached graph)
(See attached graph)
Explanation:
Given Second-Order Homogeneous Differential Equation
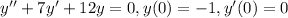
Use Auxiliary Equation
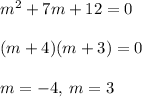
General Solution for Distinct Real Roots
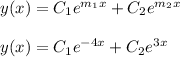
Take the derivative of y(x)
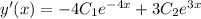
Create a system of equations given initial conditions
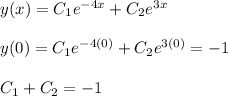
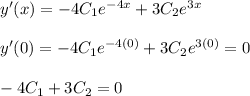
Solve the system of equations
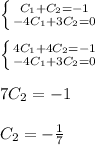
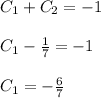
Final Solution