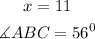Answer:
The values of x and angle ABC are;
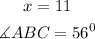
Step-by-step explanation:
From the instruction above;
Line BX bisects angle ABC.
So;
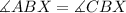
Given;
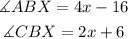
Substituting this values, we have;
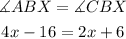
Then we can solve for x; collecting the like terms
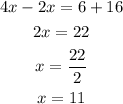
Then we can now solve for angle ABC;
Since line BX bisect angle ABC, Angle ABC equal 2 times angle ABX;
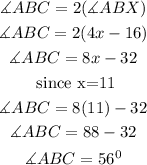
Therefore, the values of x and angle ABC are;