1) Balance the chemical equation.
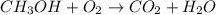
2) List the elements in the reactant and in the products.
Reactants:
C: 1
H: 4
O: 3
Products:
C: 1
H: 2
O: 3
BalanceH.
![CH_3OH+O_2\operatorname{\rightarrow}CO_2+2H_2O]()
Reactants:
C: 1
H: 4
O: 3
Products:
C: 1
H: 4
O: 4
Balance oxygen
![CH_3OH+(3)/(2)O_2\operatorname{\rightarrow}CO_2+2H_2O]()
Multiply every coefficient by the denominator
![2CH_3OH+3O_2\operatorname{\rightarrow}2CO_2+4H_2O]()
Reactants:
C: 2
H: 8
O: 8
Products:
C: 2
H: 8
O: 8
3) Moles of CH3OH needed to produce 3 mol CO2.
The molar ratio between CH3OH and CO2 is 2 mol CH3OH: 2 mol CO2.
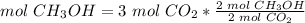
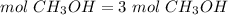
The moles of CH3OH needed are 3 mol.
.