Answer:
![\begin{gathered} a)NO_2+CO\operatorname{\rightarrow}NO+CO_2(overall\text{ react}\imaginaryI\text{on}) \\ b)NO_3 \\ c)NO_2 \\ d)R=k_1[NO_2]^2 \\ e)r=k[NO_2] \end{gathered}]()
Explanations;
Given the following sets of reaction shown below;
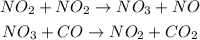
a) In order to get the overall reacton, NO2 on the reactant of the first equation will cancel out the NO2 at the product of the second reaction. The same will be applicable to NO3 in both reactions to have:
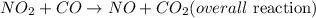
b) The intermediate ofthe reaction appears at the right side of the slow reaction first and then show upon the left side of the fast reaction. Hence the intermediate will be NO3
c) The catalyst shows in the reactant side of the slow reaction and then produced in the product of the fast reaction. Hence the catalyst from the reaction mechanism will be NO2
d) The rate law predicted by the mechanism above is given as;
![\begin{gathered} R=k_1[NO_2]^1[NO_2]^1 \\ R=k_1[NO_2]^2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/44h0ys6td4ul2c4l0z1uvujfzxkc8nivrk.png)
Note that the carbon monooxide is not part of the rate law because the order of its reaction is zero and the reaction that we used was the slow reaction (rate determining step)
e) If the reaction went in a single step, the rate law will be expressed as shown below;
![\begin{gathered} r=k[NO_2^]^1 \\ r=k[NO_2] \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/fonf9nryp3q5pspjffkhlx895pj5ig2i75.png)