Given the definition of absolute value:
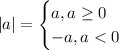
in this case we have the following:
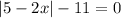
we will have two cases from this equation.
The first case is when 5-2x>=0, then we have the following:
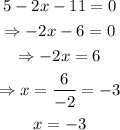
next, we will consider the cas when 5-2x < 0, then we would have the following:
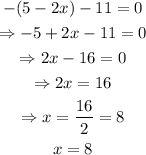
therefore, the two x-values that are solutions to the equation are x=-3 and x=8