A null hypothesis, is a hypothesis that states that there is no statistical significance between the two variables in the hypothesis. It is the hypothesis that the researcher is trying to disprove. The symbol H₀ is used to represent null hypothesis.
An alternative hypothesis states that there is statistical significance between two variables. The alternative hypothesis is the hypothesis that the researcher is trying to prove.
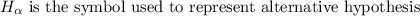
Examples:
Null Hypothesis: The world is not round.
Alternate Hypothesis: The world is round
Type 1 error is the error caused by rejecting a null hypothesis when it is true.
Type II error is the error that occurs when the null hypothesis is accepted when it is not true.
P-value is used in hypothesis testing to help you support or reject the null hypothesis. The p value is the evidence against a null hypothesis. The smaller the p-value, the stronger the evidence that you should reject the null hypothesis. If the p-value is less than or equal to alpha we reject the null hypothesis otherwise we fail to reject.
A Student t-distribution is a statistical test that compares the means of two samples. It is used in hypothesis testing, with a null hypothesis that the difference in group means is zero and an alternate hypothesis that the difference in group means is different from zero.t-test is used when sample size is small (n<50) and population variance is unknown is used when sample size is small (n<50) and population variance is unknown