Given these two series:
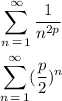
The second one is a way to write the geometric series, where r = p/2:
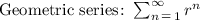
This series converges only if 0 < r < 1, so the condition of convergence of the second series is:
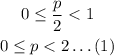
Now, for the first one, we know that the series diverges when 2p = 1, leading to the so-called Harmonic Series:
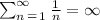
So, the condition of convergence should be:
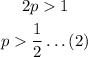
Combining these two conditions, (1) and (2), leads to:
[tex]\frac{1}{2}