The impulse I transferred by a force F to an object depends on the amount of time t during which the force acts on the object and is given by the equation:
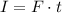
On the other hand, the force of gravity on an object with mass m is given by:
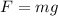
Where g is the gravitational acceleration:
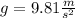
First, replace m=0.500kg and the value of g to find the force of gravity that acts on the watermelon:
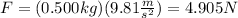
Next, replace F=4.905N and t=3.0s to find the impulse that the force gives to the watermelon in 3 seconds:
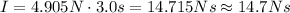
Therefore, the force of gravity acting on the watermelon for 3.0s gives it an impulse of 14.7 Ns.