1) Gases can be described with the formula below.
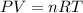
P = Pressure
V = Volume
n = moles
R = constant
T = Temperature
2) Compare the initial state and the final state.
Charles's law helps us to know the relation between Volume and Temperature. Moles and Pressure must be constant.
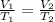
Let's work on an example: T1: 300K; V1: 20 L; T2: 320 K; V2:?
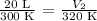
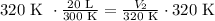
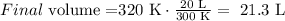
The initial volume is 20 L and the final volume is 21.3 L. This means that the volume increased when the temperature was increased.