The probability (P) an Event A or an Event B occurs is P(A) + P(B).
The probability of an event A occuring is:
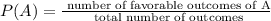
When rolling two dices, the sum can be:
If the result of the first dice is 1:
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
If the result of the first dice is 2:
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
If the result of the first dice is 3:
4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
If the result of the first dice is 4:
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10
If the result of the first dice is 5:
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
If the result of the first dice is 6:
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
Thus, there are 36 possible combinations.
From these combinations,
15 sums are less than 7
3 sums are greater than 10
Then, the probability of event A (sum is less than 7) is:
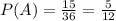
And the probability that event B (sum is greater than 10) occurs:
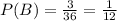
Finally:
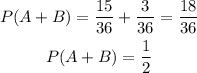
Answer: 1/2.