Step 1 - Calculate the required heat to increase the temperature to 100°C
To calculate the amount of needed heat in passing from 15°C to 100°C, we can use the following formula, relating heat and temperature increasing:
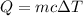
Since the density of water is 1g/ml (1000 kg/m^3), 900 ml equals 900g. The deltaT is 100 - 15 = 85°C and c is given (c = 4.2 J/g°C). Substituting these values:
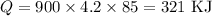
Step 2 - Calculate the heat needed to pass from liquid to vapour
We can use a similar formula, relating the needed heat to the amount of water that passed from liquid to vapour:
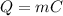
C is the latent heat of vaporization. For water, C= 2,256 J/g (2.256 KJ/Kg). Since only 8% of the water will evaporate, we have m = 72 g (8% of 900g). Substituting the values on the equation above:
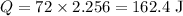
Step 3 - Sum up all heat contributions
Finally, we can sum up the values found in the previous steps:
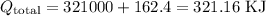
The total amount of heat that would be needed would be 321.18 KJ.