Graph Below
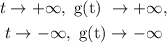
t³+2t²+t-y=2 The Standard form.
1) Let's plot that function. And then analyze the graph. We need to set a table
for t and g(t) values.
As we can see the x-intercepts are x=-2, and x=1. As the behavior we have:
As t goes infinitely positive values then g(t) or y goes the same way. When t goes infinitely negative values, y or g(t) goes the same way:
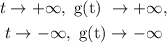
As we can see in this sketch:
The standard form is obtained from the distribution of the factors, and rewriting it as ax+by = c:
g(t)=(t-1) (t+1) (t+2)
g(t) =t³+2t²-t-2
y=t³+2t²-t-2
-t³-2t²-t+y =2
t³+2t²+t-y=2