Given:
Henry's law constant at 30 deg. celcius =4.48x10^-5 M/mmHg
Total pressure of the gases= 1 atm= 760 mmHg
Pressure of water vapor=31.8 mmHg
We will firstly determine the pressure of the carbon dioxide gas by using Dalton's Law of partial pressures:
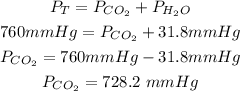
By determining the pressure of the carbon dioxide gas we can now use the Henry's Law of Gas Solubility to detemine the molar concentration:
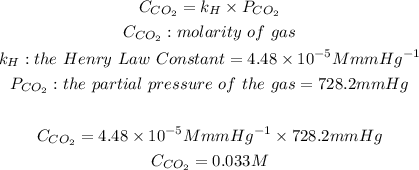
Now thaat we have the molar concentration we will convert this mass concentration:
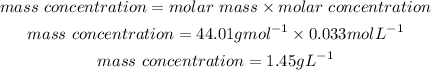
We convert this mass concentration to g/mL:
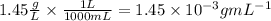
Answer: The concentration of the CO2 is 1.45x10^-3 g/mL.