We have a quadrative function defined as:
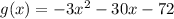
We have to find if the function has a minimum of maximum.
In general, to test for any function f(x), we have to derive the function two times and evaluate the sign of the second derivative for the value of x where we have the extreme value (that can be found as df/dx = 0).
In this case, the first derivative is:
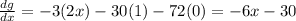
The second derivative can be now calculated as:
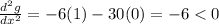
In this case we didn't need to know at which value of x we have the extreme value because the second derivative has the same sign (and value) for all values of x.
As the second derivative is negative for all values of x, this means that the first derivative has a negative slope for all values of x. This also means that the slope of g(x) is always decreasing and therfore g(x) is concave down.
If g(x) is concave down, we will have a maximum value and not a minimum.
We can now calculate where the maximum value lies by calculating x for dg/dx = 0:
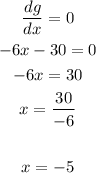
The maximum value happens at x = -5.
We can now calculate the maximum value of g(x) as g(-5):
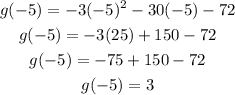
The maximum value is g(-5) = 3.
Answer:
a) We have a maximum value.
b) It happens at x = -5.
c) The maximum value is 3