The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1K.
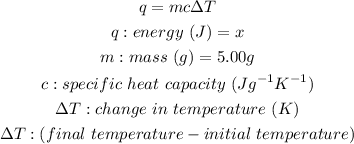
Calculating the change in temperature:
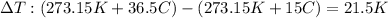
By substituting what we are given into the equation to solve for the unknow x we have;
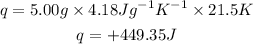
Answer: Energy needed is 449.35J