Given data
*The given speed of the cathode ray tube is v = 2.10 × 10^9 cm/s
*The given acceleration is a = 5.30 × 10^17 cm/s^2
*The given horizontal distance is d = 6.20 cm
The formula for the time taken by the electron to cover a horizontal distance is given as
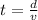
Substitute the known values in the above expression as
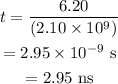
Hence, the time taken by the electron to cover a horizontal distance is t = 2.95 ns
(b)
The formula for the vertical displacement is given by the equation of motion as
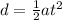
Substitute the known values in the above expression as
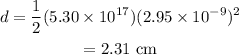
Hence, the vertical displacement during that time is d = 2.31 cm