ANSWER
4837.5 J
Step-by-step explanation
The heat needed to change the temperature of a sample of mass m of a substance whose specific heat is c is,
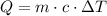
Where the change in temperature ΔT is,
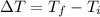
In this problem, we have a sample of copper with a mass of 0.25kg, its specific heat is 387J/(kg°C), its initial temperature is 75°C and its final temperature is 25°C. The heat for this change of temperature is,
![Q=0.25\operatorname{kg}\cdot387\frac{J}{\operatorname{kg}\cdot\text{\degree}C}\cdot(25\text{\degree}C-75\text{\degree}C)=-4837.5J]()
The result is negative, because the heat flows out of the copper, and not in.
Hence, 4837.5J flows out of the copper sample.