Given:
The tuition at a college is increasing by 5.6% each year
Let the tuition = a
So, the increases every year will form a geometric sequence
The first term = a
And the common ratio = r = 1.056
And the general term will be:
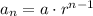
We will find the value of (n) at the term (2a)
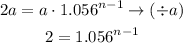
Taking the natural logarithm to both sides
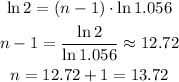
so, the tuition will be double after 13 years