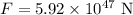The gravitational force is given by Newton's Law:
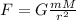
We know that in a lagrangian point the foreces cancel out, then in this case we have:
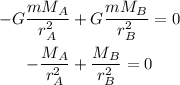
From which we can find the mass of star B:
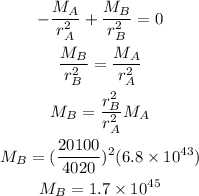
Now, that we know the mass of star B we can calculate the force exerted on star A by star B:
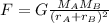
plugging the values given we have:
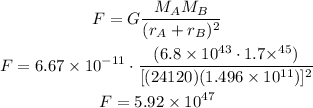
Therefore, the force exerted on star A by star B is: