The limit of a series is the value the series' terms are approaching as n goes to infinity.
We want to calculate
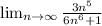
As n goes to infinity, the behavior of the denominator can be approximated in a way ignoring the constant
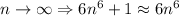
Using this approximation in our limit, we have
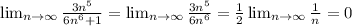
The limit of this serie is equal to zero.