Answer:
f(x) and g(x) are inverse functions because:
f(g(x)) = x and g(f(x)) = x
Step-by-step explanation:
Two functions f(x) and g(x) are inverses if g(f(x)) = x and f(g(x)) = x.
So, f(x) and g(x) are equal to:
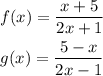
Then, to find g(f(x)), we need to replace x by f(x) on the equation of g(x), so we get:
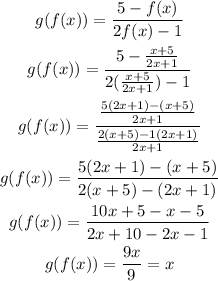
Now, we need to verify that f(g(x)) is also equal to x, so:
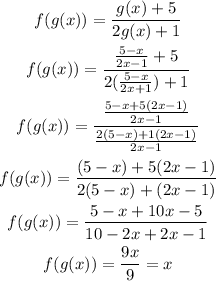
Since g(f(x)) and f(g(x)) are equal to x, we can say that f(x) ad g(x) are inverse functions.