Answer:
The velocity of the particle when it reaches the starting point = 70 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
For the first part of the motion
The initial velocity, u = 10 m/s
The final velocity v = 50 m/s
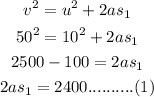
For the second part of the motion
The initial velocity, u = 50 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0 m/s
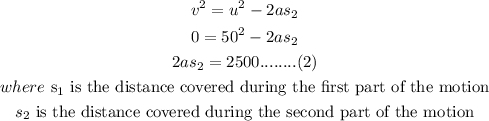
Add equations (1) and (2)
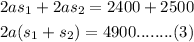
Taking the whole motion as a whole
Let the velocity of the particle when it reaches the starting point be vn
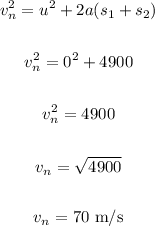
The velocity of the particle when it reaches the starting point = 70 m/s