Answer:
1i) P(A) = 1/2
ii) P(B) = 1/2
iii) P(A and B) = 1/4
2) P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B) = 3/4
3) P(A or B)/ P(A U B)
Explanations:
Probability is the likelihood or chance that an event will occur. Mathematically;
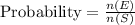
n(E) is the number of events
n(S) is the total sample space
An 8-sided die with faces labeled 1 to 8 will be rolled once, the sample space will be S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
n(S) = 8
a i) For event A, we need to get the number of outcome greater than 4.
A = {5, 6, 7, 8}
n(A) = 4
P(A) = n(A)/n(S)
P(A) = 4/8 = 1/2
ii) For event B, we need the outcomes that gives an even number.
B = {2, 4, 6, 8}
n(B) = 3
P(B) = n(B)/n(S)
P(B) = 4/8 = 1/2
iii) For the probability of the event of rolling a number greater than 4 and rolling an even number,
P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
P(A and B) = 1/2 * 1/2
P(A and B) = 1/4
2) To compute P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B), we will substitute resulting probabilities in (a) into the expression as shown:
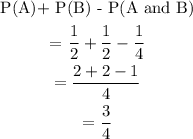
Hence P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B) = 3/4
3) Note that P(A and B) can also be written as P(A n B) and according to set theory;
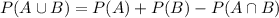
This can be also be expressed as:
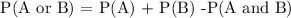
Hence from these two notations, we can see that the answer that makes the equation true is P(A or B)/P(A U B)