Pent-1-ene reacts with hydrogen bromide as follows:
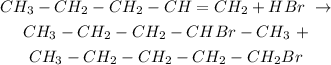
The two products fromed are:
2-bromopentane and 1-bromopentane respectively.
The major product that is formed in the reaction is 2-bromopentane and this can be explained because the carbocation that is created during the reaction is more stable than the one that is form during the reaction that produces 1-bromopentane.
The reaction that formes 2-bromopentane follows Markovnikov's Rule. This rule sais:
When a compound HX (in this case HBr) is added to an unsymmetrical alkane (in this case pent-1-ene), the hydrogen becomes attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens attached to it already.
The mechanism of the reaction that forms 2-bromopentane is the following, and it is called an electrophilic addition.
Step 1: Pent-1-ene is protonated and it gives rise to the more stable secondary carbocation.
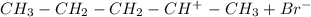
Step 2: The bromide ion reacts with the carbocation forming 2-bromopentane.
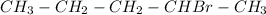
The other carbocation that can be formed is the primary carbocation:
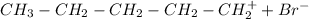
That later reacts with the bromide ion to form 1-bromopentane. However, as the secondary carbocation is more stable that the primary carbocation the major product of the reaction is 2-bromopentane.