Answer:
115.25g/mol
Explanations:
According to the ideal gas equation:
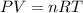
where
• P is the ,pressure (,in atm)
,
• V is the ,volume ,in litres
,
• n is the ,number of moles
,
• R is the ,Gas constant
,
• T is the ,temperatur,e in kelvin
Recall that:
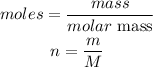
Substitute into the ideal equation to have:
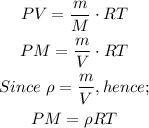
The expression for calculating the molar mass will be:
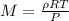
Given the following parameters
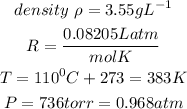
Substitute the given parameters into the formula
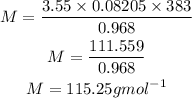
Hence the molar mass of the gas will be approximately 115.25g/mol