SOLUTION
Given the question in the image, the following are the solution steps to answer the question.
STEP 1: Write the given functions
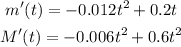
STEP 2: Find m'(20) for subject A
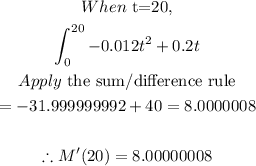
STEP 3: Find M'(20) for subject B
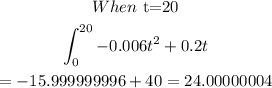
STEP 4: Find how many more words subject B memorizes more than subject A
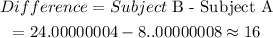
Hence, Answer is approximately 16 words