Answer:
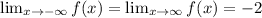
Explanation:
Given a rational function, the end behavior of its graph is how the graph behaves as x approaches infinity or negative infinity.
In the function f(x) below:
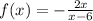
• The degree of the numerator = 1
,
• The degree of the denominator = 1
Since the degrees of the numerator and the denominator are the same, divide the coefficients of the leading terms to obtain the horizontal asymptote.
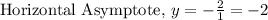
Thus, for f(x):
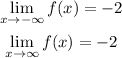
The function approaches -2 as x tends to positive and negative infinity.
Next, we determine the vertical asymptote of f(x) by setting the denominator equal to 0 and solving for x.
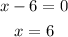
What this means is that in f(x), the value of f(x) is undefined at x=6.