Given data
*The given mass of the iron is m_i = 0.350 kg
*The given initial temperature of the iron is T_i = 465 °C
*The given mass of the water is m_w = 21.4 kg
*The given initial temperature of the water is T = 21.2 °C
*The value of the specific heat of water is c_w = 4186J/kg.°C
*The value of the specific heat of iron is c_i = 448J/kg.°C
The total energy input from the surrounding is equal to zero. It is given as
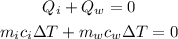
Substitute the known values in the above expression as
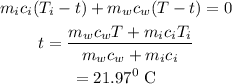
Hence, the final equilibrium temperature (in °C) is t = 21.97°C