We have the combustion reaction of benzene, the balanced equation of the reaction is:
2C6H6(l) + 15O2(g) → 12CO2(g) + 6H2O(l)
We see that for every two moles of benzene, 15 moles of oxygen are needed, so the ratio O2 to C6H6 is 15/2.
Therefore, the moles of oxygen will be:
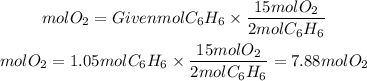
To calculate the volume of oxygen, since oxygen is a gas, we will apply the ideal gas law which tells us:
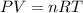
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas = 1atm
T is the temperature of the gas = 0°C =273.15K
n is the moles of the gas = 7.88molO2
R is a constant = 0.08206 atm.L/mol.K
We clear the volume, and replace the known data:
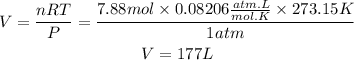
Answer: The volume of oxygen gas required to react completely with 1.05 mol of benzene is 177 Liters oxygen gas