Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to calculate the change in enthalpy of the given reaction
To get that, we are going to use the 3 related equations below it
We proceed as follows:
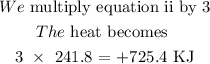
We arrange equation 1 in the opposite direction
This makes the heat become:
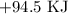
For equation iii, we arrange in opposite direction too
The heat becomes:
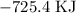
We can now begin to make additions and subtractions as follows:
![undefined]()