Given,
The mass of the iron, m=100 kg
The initial temperature of the iron, T₁=25 °C=298.15 K
The melting point of the iron, T₂=1538 °C=1811.15 K
The specific heat of the iron, c=4.5×10² J/kg°C
The latent heat of fusion of iron, L_f=2.66×10⁵ J/kg
The heat needed to raise the temperature of the iron to 1811.15 K is given by,
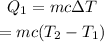
The heat required to change the phase of the iron from solid to liquid is
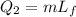
Thus the total heat required is,
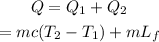
On substituting the known values,
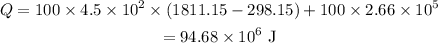
Thus the thermal energy that must be supplied is 94.68×10⁶ J