The instantaneous rate of change is the derivative of the function so lets calculate it:
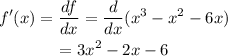
Now that we know the derivative to find the instantaneous rate at a given value we just evaluate it at that point.
a)
If x=-1, then:
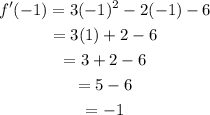
Therefore the instantaneous rate of change at x=-1 is -1.
b)
If x=4, then:
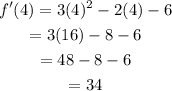
Therefore the instantaneous rate of change at x=4 is 34.