Step 1
The gas is assumed to be ideal. Therefore, the next formula is applied:
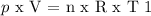
------------------------------------------------
Step 2
Information provided:
p = pressure = 147 kPa x (1000 Pa/1 kPa) = 147000 Pa
V = volume = unknown
n = number of moles = 2.10 moles
T = absolute temperature = 340.0 K
R = gas constant = 8.314 m^3 x Pa/mol K (according to the variables and units provided)
-------------------------------------------------
Step 3
Procedure:
V is found from (1):
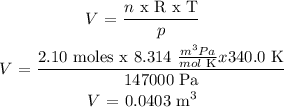
Next, V = 0.0403 m^3 x (1000 L/1 m^3) = 40.3 L
Answer: V = volume = 40.3 L