Given the function
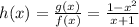
Notice that
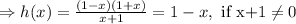
Then, h(x) has a removable discontinuity at x=-1
a) To find the zeroes of the function solve h(x)=0, as shown below,
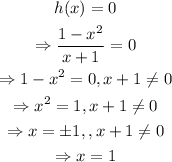
Thus, the zero of the function is at x=1.
b) There are no asymptotes, only a removable discontinuity as shown above.
c) The domain of h(x) consists of the values of x such that the denominator is different than zero
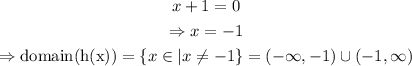
As for the range of the function, as we established before,
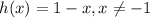
And the range of 1-x is the set of real numbers. Therefore, the range of the function is
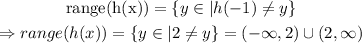
d) There is a discontinuity at x=-1, although it is 'removable'.
e) Except for the point x=-1, h(x) is well defined for any other value of x. The answer to part e) is x=-1, y=2. (-1,2) is the only point that is not included in the domain nor the range of the rational function