Answer:
397 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Recall the ideal gas law:
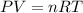
If temperature and pressure stays constant, we can rearrange all constant variables onto one side of the equation:
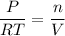
The left-hand side is simply some constant. Hence, we can write that:
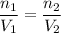
Substitute in known values:
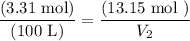
Solving for V₂ yields:
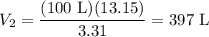
In conclusion, 13.15 moles of argon will occupy 397* L under the same temperature and pressure.
(Assuming 100 L has three significant figures.)