Given: An absolute inequality
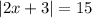
Required: To solve the given absolute inequality.
Step-by-step explanation: The absolute rule states
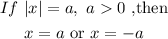
Hence for the given problem, we have
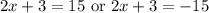
Solving these two equations
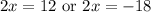
Which gives the value of x as
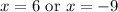
Hence the equation given can have two solutions.
Final Answer: The given equation can have two solutions as x=6 or x=-9.