We are given that a person tosses a coin twice. A tree of possible outcomes is the following:
Where "H" is head and "T" is tails.
The possible outcomes are then:
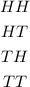
There are 4 possible outcomes.
Part 2. To determine the probability of getting two tails we notice that from the 4 possible outcomes 1 is TT, therefore, the probability is:
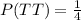
The probability of getting two heads is determined also using the fact that from the 4 possible outcomes only one is HH, therefore:
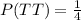
This means that the probabilities are the same.
The reason why he didn't get the exact number of times as predicted might be due to the fact there might be other variables affecting the outcome. Or that can be due to the fact that the number of tosses is not enough to see a tendency.