2, a)
Given:
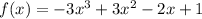
Aim:
We need to find the end behavior, the maximum number of x-intercepts, the existence of a maximum or minimum value of the given functions.
Step-by-step explanation:
Use graphing technology.
The graph of the given function is
One end of the curve is moving upward to infinity when x tends to negative infinity and another end is moving down to negative infinity when x tends to infinity.
Take the limit to infinity on the given function to find the end behavior.
![\lim_(x\to\infty)f\mleft(x\mright)=\operatorname{\lim}_(x\to\infty)\mleft(-3x^3+3x^2-2x+1\mright)]()
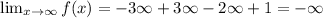
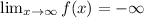
Take limit to negative infinity on the given function to find the end behavior.
![\lim_(x\to-\infty)f\mleft(x\mright)=\operatorname{\lim}_(x\to-\infty)\mleft(-3x^3+3x^2-2x+1\mright)]()
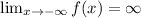
End behavior:
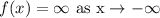
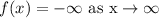
We know that the x-intercept is the intersection point where the function f(x) crosses the x-axis.
The x-intercepts = (0.718.0)
Differentiate the given function with respect to x and set the result to zero.
Solve for x to find the existence of a maximum or minimum value of the given function.
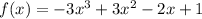
Differentiate the given function with respect to x
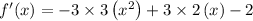
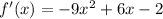
SEt f'(x) =0 and solve for x.
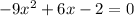
Multiply both sides by (-1).
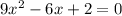
which is of the form
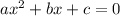
where a =9, b=-6 and c=2.
Use quadratic formula.
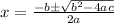
Substitute a =9, b=-6, and c=2 in the equation.
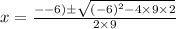
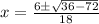
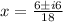
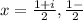
We get a complex value for x.
There is no maximum or minimum value of the given function in a real number.
Final answer:
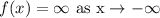
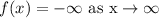
The x-intercepts = (0.718.0)
There is no maximum or minimum value for the given equation.