1) Balance the chemical equation.
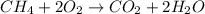
2) Convert the mass of CH4 to moles of CH4.
The molar mass of CH4 is 16.0425 g/mol.
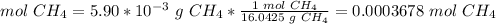
3) Moles of CO2 produced from CH4.
The molar ratio between CH4 and CO2 is 1 mol CH4: 1 mol CO2.
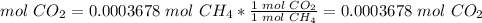
4) Convert moles of CO2 to mass of CO2.
The molar mass of CO2 is 44.0095 g/mol.
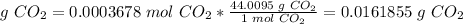
The mass of CO2 produced from 5.90*10^-3 g CH4 is 0.0162 g CO2.
.