Answer:
• The radius of convergence is 2.
,
• The interval of convergence is (2,6).
Explanation:
Given the series:
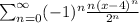
We can rewrite it in the form below:
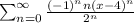
We apply the ratio's test to find the radius of convergence:
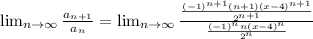
First, simplify the fraction:
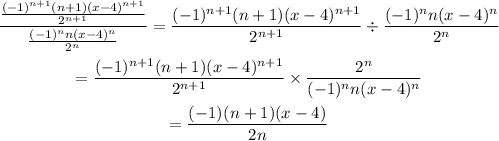
Therefore:
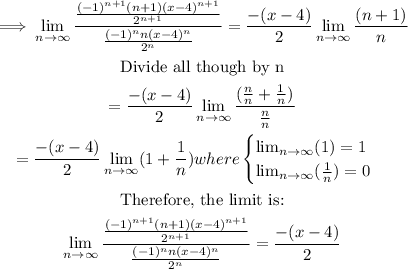
In order for the series to converge, we need:
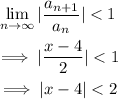
The radius of convergence is 2.
[tex]\begin{gathered} |x-4|<2 \\ -2
The interval of convergence is (2,6).