ANSWER
ΔU = 0
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
• The charge of the particle at the origin, q₁ = 5.5*10⁻⁸ C
,
• The charge of the particle at the point (3.5 cm, 3.5 cm), q₂ = -2.3*10⁻⁸ C
Unknown:
• The change in potential energy of the system, ΔU (this is what we have to find)
By conservation of energy, the potential energy must be equal to the work done to move the particle,
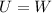
Work is the product of distance and the force applied,
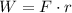
By Coulomb's Law, the force of attraction/repulsion between two particles separated a distance r is,
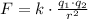
Thus, the potential energy is,
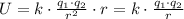
At first, the second particle was at x = 3.5 cm and the final position was at y = 3.5 cm,
The change in potential energy is the difference between the final and initial potential energy of the system,
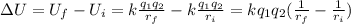
Before doing any calculations, note that the distance between the two particles is the same for both positions of the second particle: 3.5cm. Thus, the difference between the reciprocals of the distances is zero and, therefore, the change in potential energy is zero.