The potential difference is 14.4 V.
Given data:
The length of wire is l=100 m.
The resistivity of the copper is ρ=1.70x10^-8 Ωm.
The diameter of wire is d=1.50 mm.
The current in the wire is I=15 A.
The resistance of the wire can be calculated as,
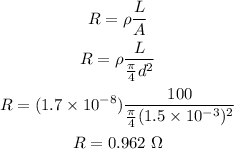
The potential difference can be calculated using the Ohm's law,
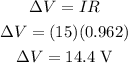
Thus, the potential difference is 14.4 V.