Given
![f\mleft(x\mright)=x^3-2x²+x+1,\left[-2,2\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/lvt9ekpwgy2nw72eq3152e0vs5aipq7c8s.png)
Find
value of c
Step-by-step explanation
mean value theorem states that " Let f be continuous over the closed interval [a , b] and differentiable over the open interval (a , b). Then , there exist atleast one poin c which belongs to (a , b) such that
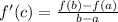
so ,
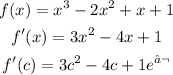
and
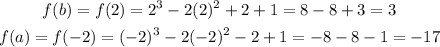
so ,
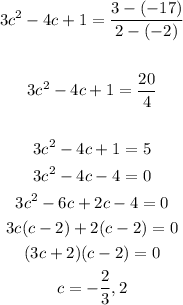
Final Answer
Therefore , the values of c are -2/3 and 2