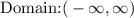Answer:
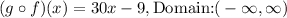
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the functions f(x) and g(x) defined as follows:
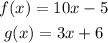
The composite function g o f is defined below:
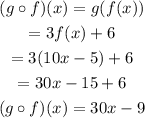
The domain of the function is the set of all possible values of x.
In the composite function, x can take on any value in the real line. Therefore: