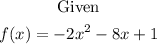
First, find the vertex of the given function, we have

Next, substitute x = -2. to the given function and we get
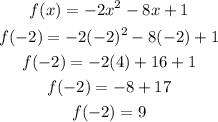
Therefore, the vertex is at (-2.9).
The axis of symmetry is at x = -2.
The y-intercept at y = 1.
The x-intercepts are the following:
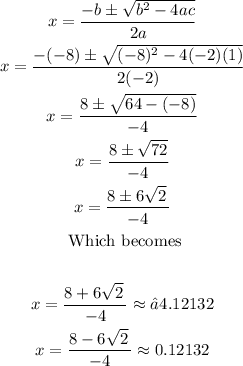
Graphing the function we get