Since KOH dissolves in water so KOH is solute while water is solvent.
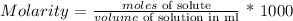
Now, we need to calculate moles of solute (KOH)
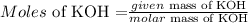
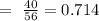
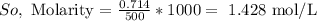
Now, we need to dilute the solution, so we will use molarity equation for dilution which is M1V1 = M2V2
Here, M1= 1.428 M; V1= 40 ml; M2 = 1 M; we need to find V2
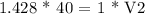
Therefore, V2 = 57.12 ml